What is Forex Trading?
Discover what Forex trading is, how it works & why it’s the largest financial market..
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the global marketplace for buying and selling currencies. This guide explains the fundamentals of forex trading, how the market operates, and the key concepts every trader should understand before trading Forex CFDs with Ohio Markets.
What Is Forex (FX) Trading?
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another with the objective of profiting from changes in exchange rates. Unlike stock markets, which trade through centralised exchanges, forex trading takes place over-the-counter (OTC). This means transactions are conducted electronically through a global network of banks, financial institutions, central banks, governments, corporations, and retail traders.
Governments and central banks participate in the forex market to manage currency reserves, control inflation, and influence monetary policy. Banks and financial institutions provide liquidity and facilitate global currency transactions.
Due to its high liquidity and global participation, the forex market is the most actively traded financial market in the world. It enables businesses to conduct international trade, investors to hedge against currency risks, and traders to speculate on currency price movements.
How Forex Trading Works?
Forex trading operates through a decentralised global market where currency prices fluctuate based on supply and demand, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
For example, if you believe the GBP/USD exchange rate will rise, you may choose to buy GBP and sell USD. If you enter the trade at 1.3000 and the price rises to 1.3100, you can close the trade at a profit. However, if the price falls to 1.2900, you would incur a loss.
When trading Forex CFDs with a broker like Ohio Markets, it is important to understand trading costs such as spreads, commissions, and overnight financing fees. Trading forex also involves risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment if risk management is not applied properly.
Understanding Currency Pairs
Forex trading always involves currency pairs, where one currency is bought and another is sold.
Base currency: The first currency in the pair
Quote currency: The second currency in the pair
Example: EUR/USD
Base currency: Euro (EUR)
Quote currency: US Dollar (USD)
The exchange rate shows how much USD is required to buy one EUR.

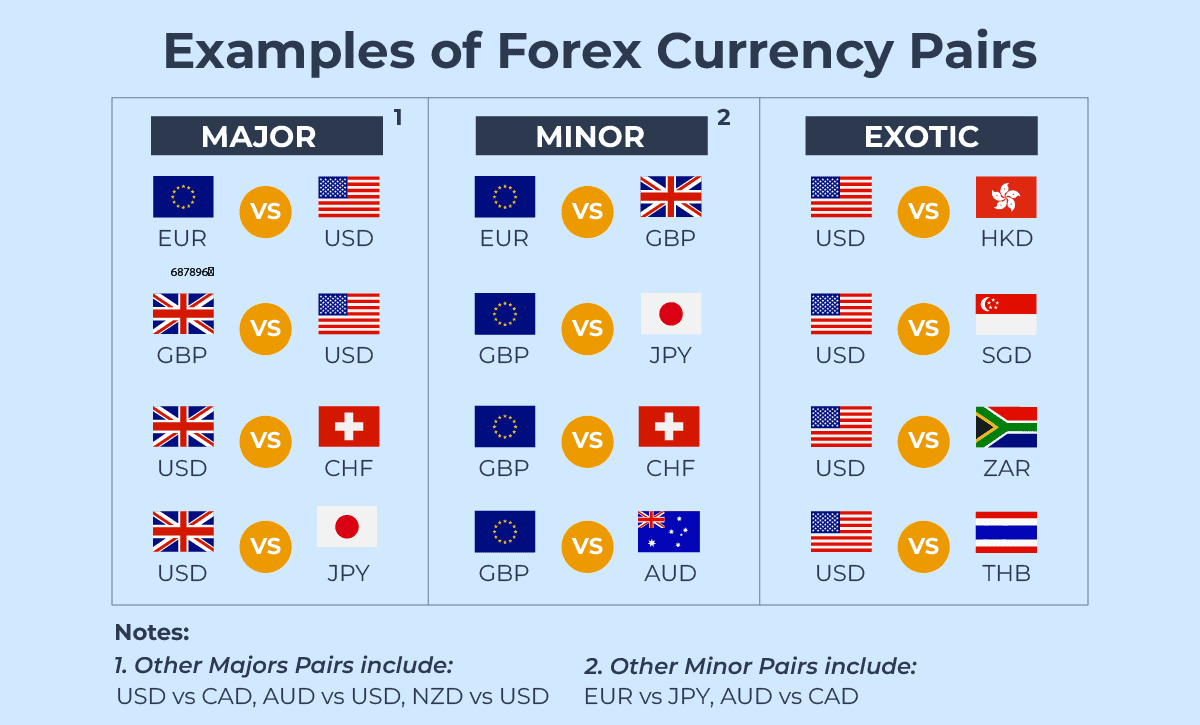
Major Currency Pairs
Major currency pairs are the most traded pairs globally and typically offer high liquidity and lower spreads.
| Pair | Name | Nickname |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | Euro Dollar | Fiber |
| USD/JPY | Dollar Yen | Gopher |
| GBP/USD | Pound Dollar | Cable |
| USD/CHF | Dollar Swiss | Swissie |
Minor and Exotic Currency Pairs
Minor pairs do not include the US dollar (e.g. EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY).
Exotic pairs combine a major currency with an emerging market currency (e.g. USD/TRY, EUR/ZAR).
These pairs often experience higher volatility and wider spreads compared to major pairs.
Key Forex Trading Concepts Explained
Understanding core forex terminology is essential for managing risk and making informed trading decisions.
Spreads and Pips
Spreads
The spread is the difference between the buy (ask) price and the sell (bid) price of a currency pair. It represents the primary trading cost and may be fixed or variable depending on market conditions.
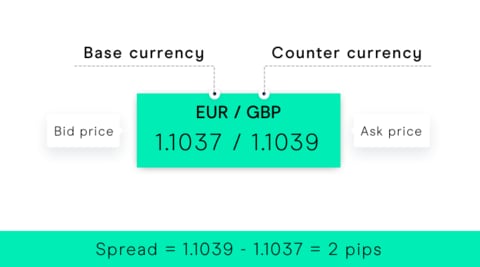
Pips
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement in a currency pair.
Most pairs: 4th decimal place
JPY pairs: 2nd decimal place
Example:
If EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005, the price has moved 5 pips.
Leverage and Margin
Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions using a smaller amount of capital. It is expressed as a ratio, such as 10:1, 20:1, or 30:1.
For example, with 30:1 leverage, a trader can control a $30,000 position with $1,000 in margin. While leverage can increase potential profits, it also significantly increases risk and potential losses.
Margin
Margin is the amount of capital required to open and maintain a leveraged trade. If losses exceed a certain level, the broker may issue a margin call or automatically close positions to prevent further losses.

Example: How Leverage Works in Forex
Assume you have $1,000 in your trading account and open a $30,000 EUR/USD position using 30:1 leverage at 1.1000.
If price rises to 1.1050 (50 pips):
Profit = $150If price falls to 1.0950 (50 pips):
Loss = $150
Without proper risk management, losses can exceed your deposit. This is why tools such as stop-loss orders and negative balance protection are essential.
Regulated Broker
Segregated Client Funds
Insurance Protection
Global Traders
What Are Lots in Forex Trading?
A lot defines the size of a forex trade.
Standard lot: 100,000 units
Mini lot: 10,000 units
Micro lot: 1,000 units
Nano lot: 100 units
Smaller lot sizes allow traders with lower capital to manage risk more effectively.

What Moves the Forex Market?
Forex prices are influenced by several key factors:

Economic Indicators
Data such as GDP, inflation, employment figures, and consumer spending can impact currency values. Strong economic data often supports a stronger currency.
Central Bank Policies
Interest rate decisions, monetary policy statements, and market interventions by central banks play a major role in currency movements.
Geopolitical Events
Political instability, elections, trade disputes, and global crises can lead to increased market volatility.
Market Sentiment
Investor confidence, speculation, and risk appetite influence demand for currencies. During uncertainty, traders often move toward safe-haven assets like the US dollar.
What Is a Forex Broker?
A forex broker provides traders with access to the forex market through online trading platforms. Brokers facilitate trades, offer leverage, and provide trading tools. Revenue is typically generated through spreads, commissions, or overnight fees.
Risks and Rewards of Forex Trading
Forex trading offers opportunities, but it also involves significant risk.
Potential Rewards
High liquidity allows fast trade execution
Ability to profit in rising and falling markets
Access to leverage for greater market exposure
Potential Risks
High volatility can cause rapid losses
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses
Unexpected economic or geopolitical events may impact prices
Explore More About Forex Trading
Why Trade with Us?
Trade with a Forex broker that ensures the highest market standards for your trading convenience.
Be Confident, Be Sure


Trade with confidence
150+ countries
24/7 support

Your Trading journey is safe and secure
200+ payment methods
Trust We Have Earned














